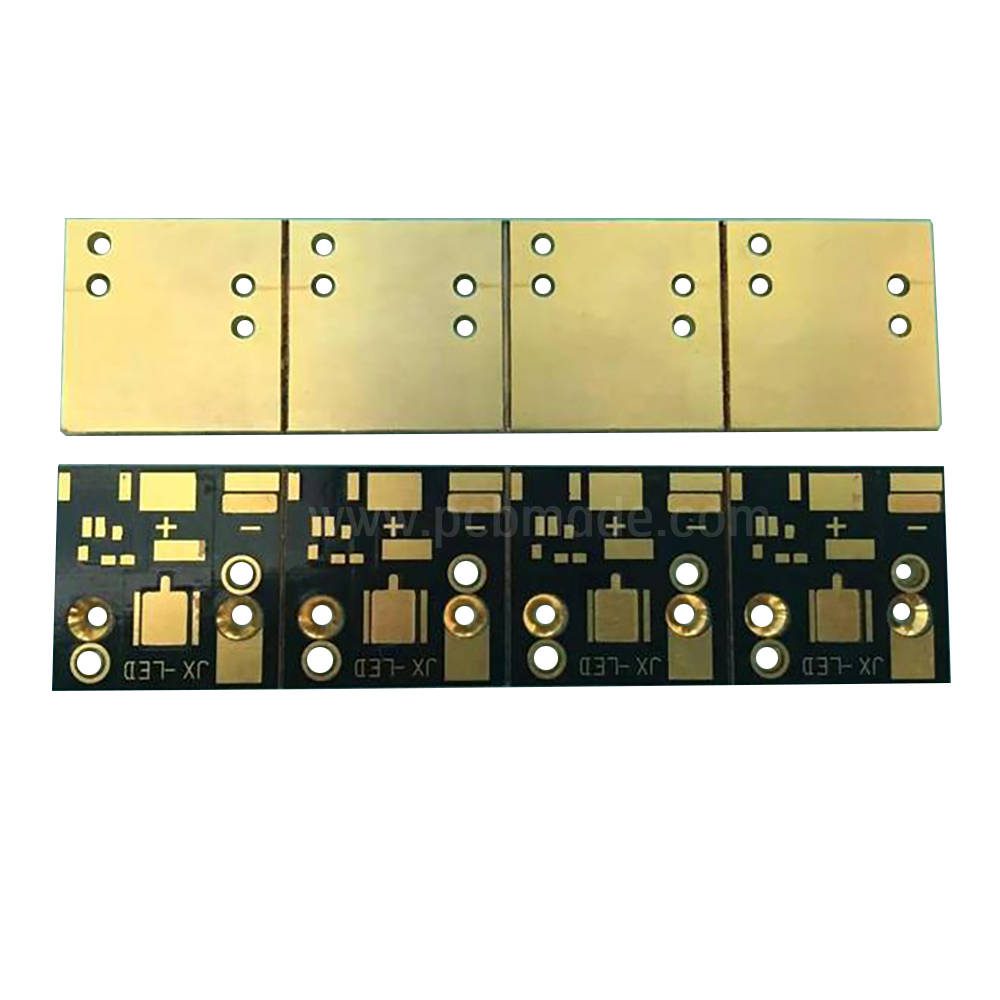
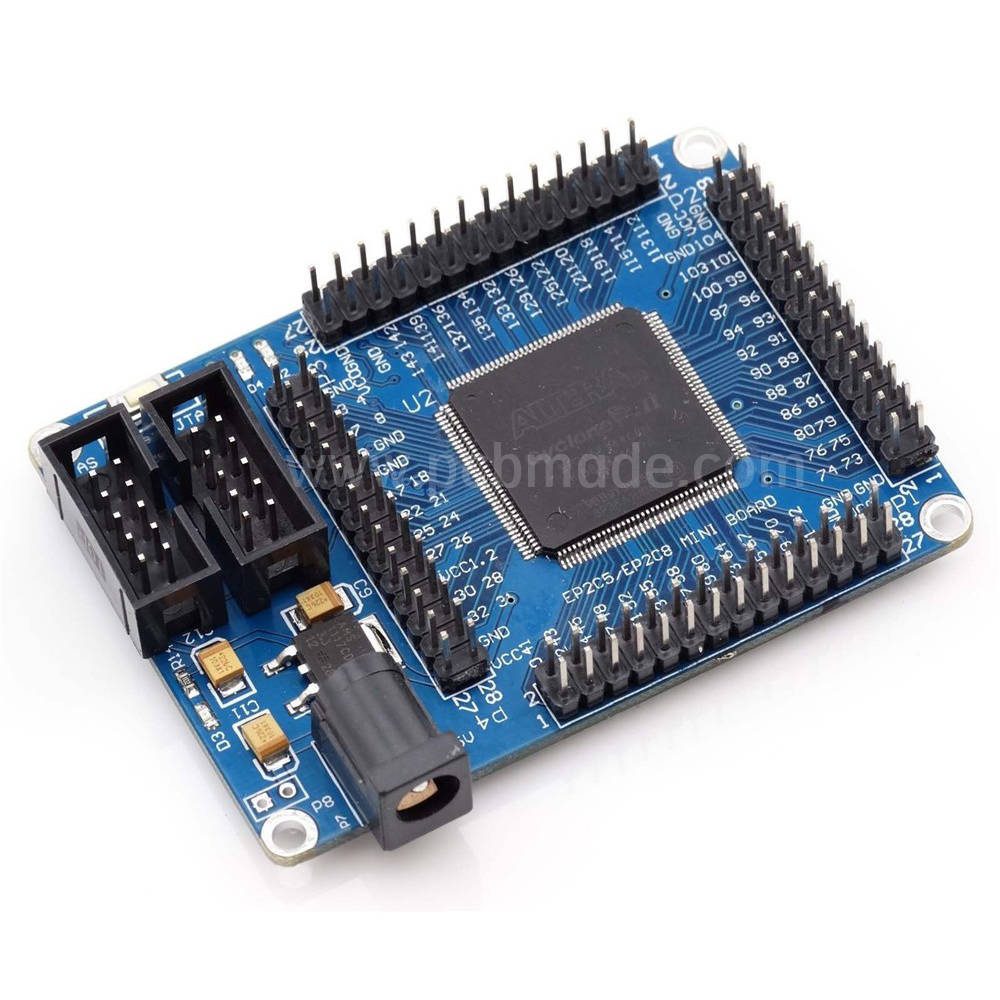
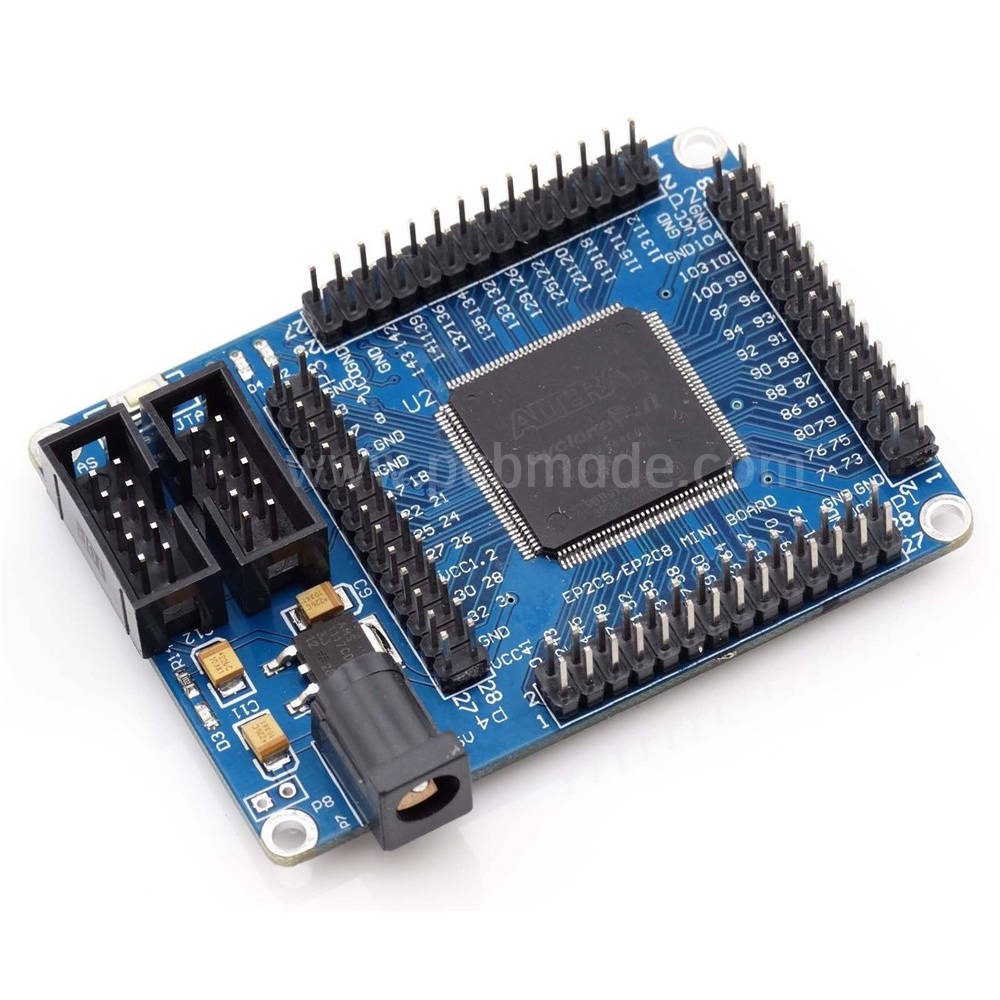
PCB is the core component of electronic devices, and as the cornerstone of precision circuit board technology, the quality of PCB directly affects the performance and reliability of products.
In the PCB manufacturing process, copper foil blistering is a common but not negligible problem, which not only affects the electrical performance of the circuit, but may also reduce the overall quality and lifespan of the product.
The function of PCB and copper foil
Firstly, let’s briefly understand the basic composition of PCB. PCB is mainly composed of an insulating substrate, a copper foil layer, and a protective layer. The copper foil layer is responsible for carrying current and forming circuit patterns, while the insulating substrate provides support and isolates each circuit layer, and the protective layer protects the circuit from environmental factors. The quality and bonding state of copper foil are directly related to the conductivity and stability of the circuit.
Analysis of the causes of copper foil bubbling
During the PCB production process, the phenomenon of copper foil bubbling is usually caused by the following factors:
Moisture absorption: During storage or pre-treatment, if copper foil or substrate material is exposed to a humid environment, it will absorb moisture from the air. When these materials enter the high-temperature baking or welding process, the internal moisture evaporates to form steam, and the pressure increases, causing bubbles to form between the copper foil and the substrate or inside the copper foil.
Insufficient cleanliness: Contaminants such as grease and dust on the surface of the substrate or copper foil can affect the adhesion between the copper foil and the substrate. In the subsequent heat treatment process, these impurities may become the starting point for foaming.
Improper process parameters, including but not limited to improper settings of pressing temperature, time, pressure, etc., may lead to insufficient adhesion between copper foil and substrate, leaving space for the formation of bubbles.
Material compatibility issue: Different types of substrates and copper foil materials may have different coefficients of thermal expansion. When the temperature changes, this mismatch may cause internal stress concentration, leading to foaming.
Manufacturer’s response strategy
Faced with the challenge of copper foil blistering, professional PCB manufacturers have adopted various strategies to ensure product quality:
Strictly control environmental humidity: Before storing and processing raw materials, ensure that the environment is dry, use dehumidification equipment, and perform necessary pre drying treatment on the materials to reduce moisture content.
Strengthen cleaning process: Use efficient cleaning agents and equipment to thoroughly remove contamination on the surface of substrates and copper foils, ensuring a good bonding foundation.
Optimize process parameters: By precisely controlling the pressing temperature, time, and pressure, as well as selecting appropriate pressing equipment, ensure stable adhesion between copper foil and substrate.
Material compatibility testing: In the early stages of product design, material compatibility testing is conducted by selecting substrates and copper foils with matching thermal expansion coefficients to reduce internal stress caused by material mismatch.
Advanced detection technology: utilizing high-precision detection methods such as X-ray inspection and optical microscopy to promptly detect and eliminate potential foaming hazards, ensuring product quality.
Although the foaming of PCB copper foil is small, it can significantly affect the final performance and reliability of the product. By deeply analyzing the causes of foaming and taking targeted preventive measures, PCB manufacturers can effectively control this problem and ensure high-quality production of electronic products. With the continuous advancement of technology and the continuous optimization of production processes, the manufacturing of PCBs in the future will be more efficient and reliable, laying a solid foundation for the innovative development of electronic technology.