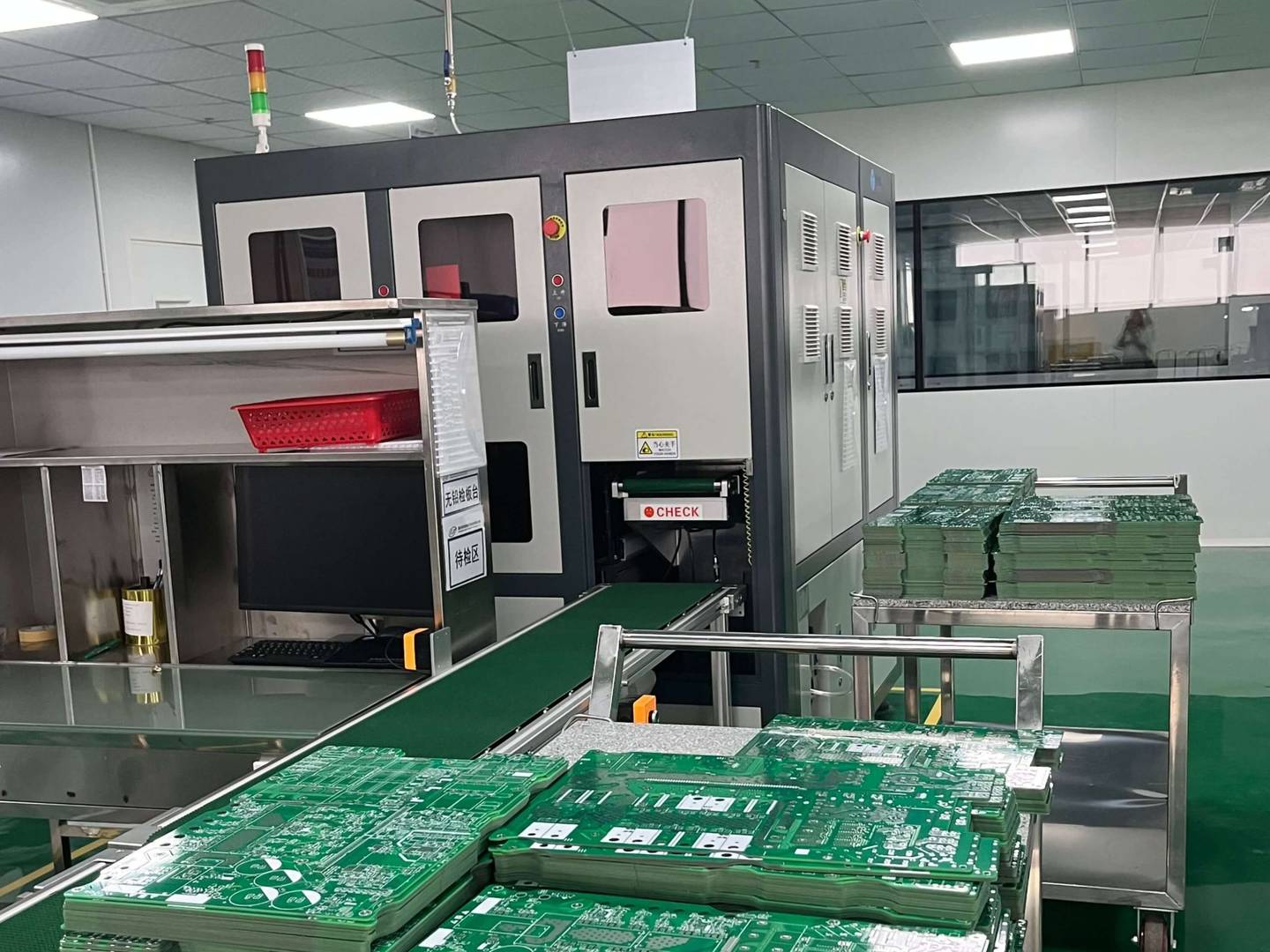
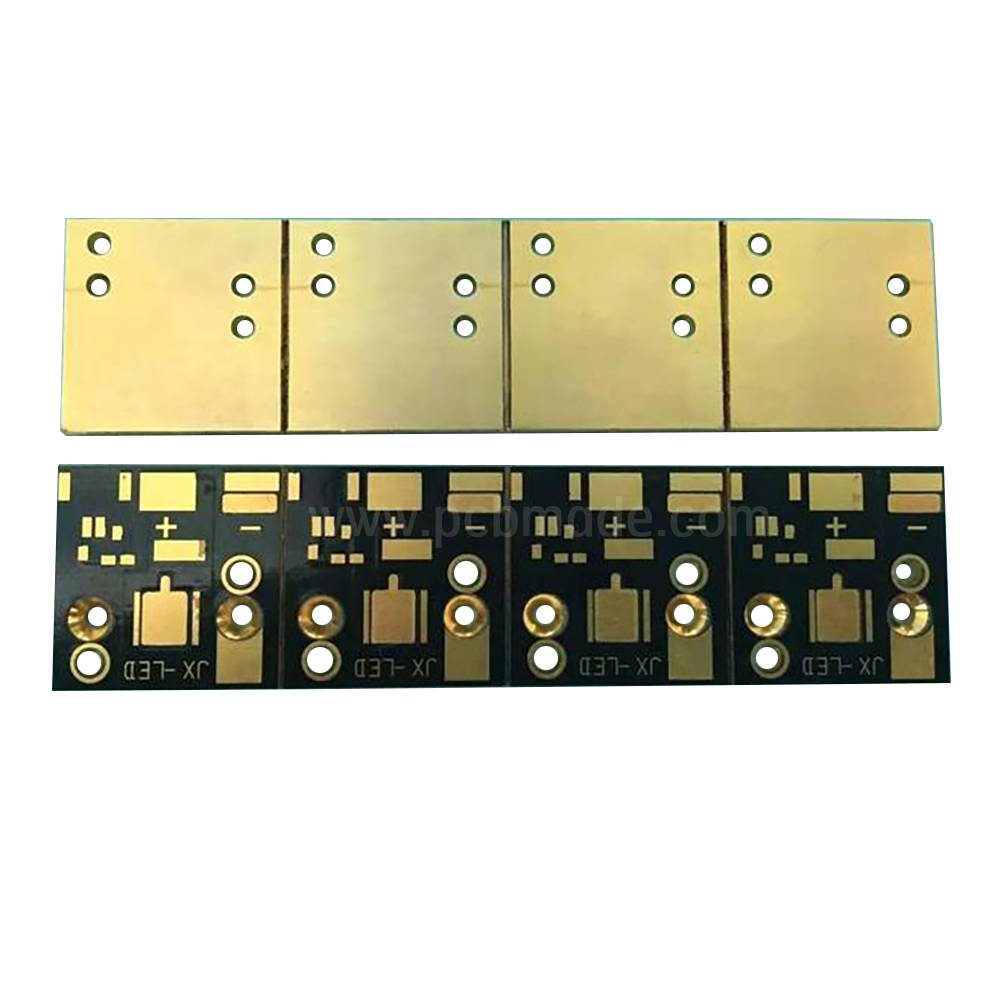
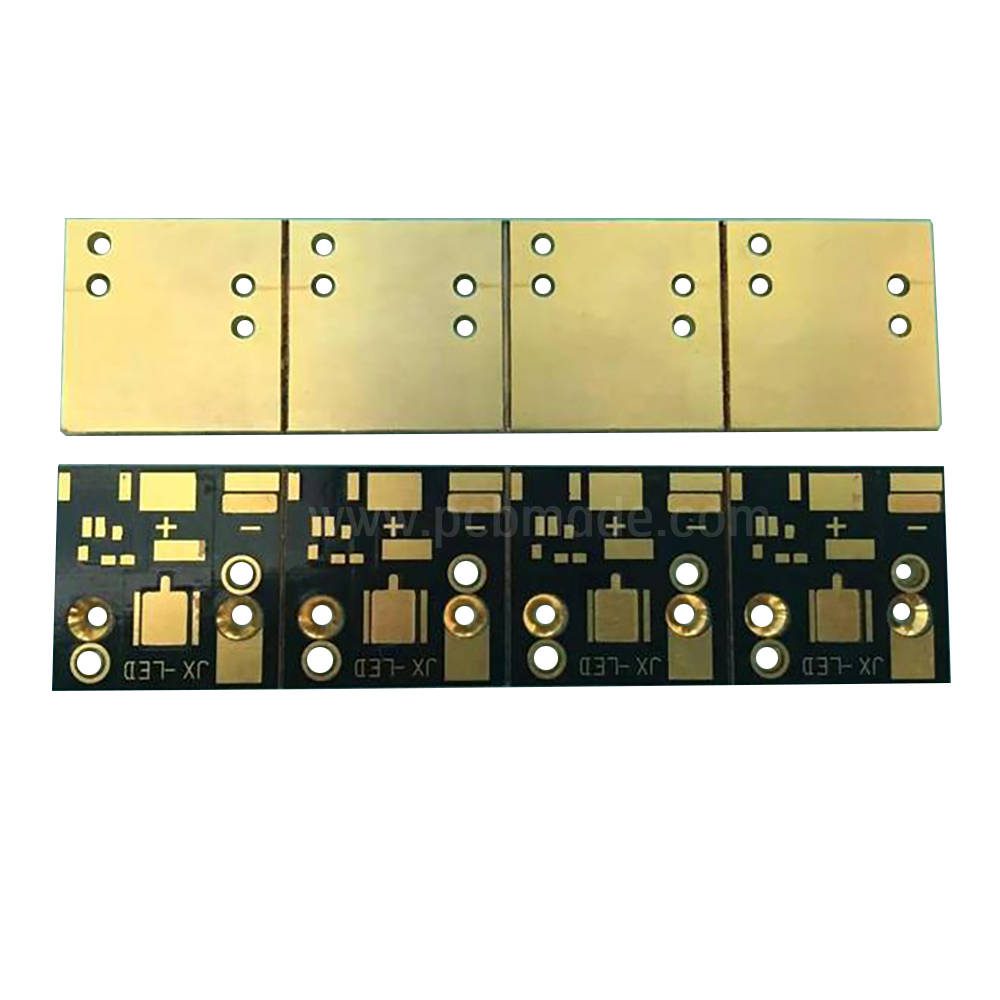
In the manufacturing process of PCB (Printed Circuit Board), splicing refers to the method of combining multiple PCB boards together for processing. Splicing can improve production efficiency, reduce costs, and is suitable for large-scale production.
The PCB assembly methods are mainly divided into the following types:
1. Rigid panel assembly: Multiple rigid PCB boards are fixed together by mechanical or adhesive means. This method is suitable for applications that require high mechanical strength and stability, such as industrial control equipment, communication equipment, etc.
2. Flexible PCB splicing: Fixing flexible PCB boards together by mechanical or adhesive means. Flexible panel can be bent and folded, suitable for applications that require bending or compact design, such as mobile devices, wearable devices, etc.
3. Rigid flexible combination splicing: Fix rigid PCB boards and flexible PCB boards together by mechanical or adhesive means. This approach combines the characteristics of rigidity and flexibility, and is suitable for applications that require both mechanical strength and flexibility design, such as automotive electronics, medical equipment, etc.
4. Multi layer PCB assembly: Multiple PCB boards are fixed together by mechanical or adhesive means and connected through inner layer circuits. Multilayer panel can provide higher circuit density and signal transmission performance, suitable for high-performance electronic devices such as computers, servers, etc.
5. Stacking and splicing: Multiple PCB boards are stacked together mechanically or with adhesive, and connected through through holes or blind holes. Stacked panel can provide higher signal transmission speed and circuit density, suitable for high-speed communication devices such as network switches, routers, etc.
Choosing the appropriate splicing method needs to be determined based on specific application and design requirements, while also considering production processes and cost factors.